Initiation aux CTFs
THM Room https://tryhackme.com/room/ecolecybertraining
TASK 1 : Introduction
Prêt.e?
No Answer
TASK 2 : Pré-CTF
Lu
No Answer
TASK 3 : Web
Dans cette section, nous allons démystifier cette technologie qui a changé le monde à tout jamais.
No Answer
TASK 4 : Web - Outils
Quel élément est ajouté au début de l’URL lorsqu’on affiche le code source?
For this use right click on the page then “view page source” :
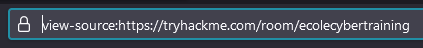
Then check the URL :
Answer : view-source:
Quel est la balise utilisé par les hyperliens (Si ça aurait été h1 (celui du titre) vous aurez répondu <h1>)
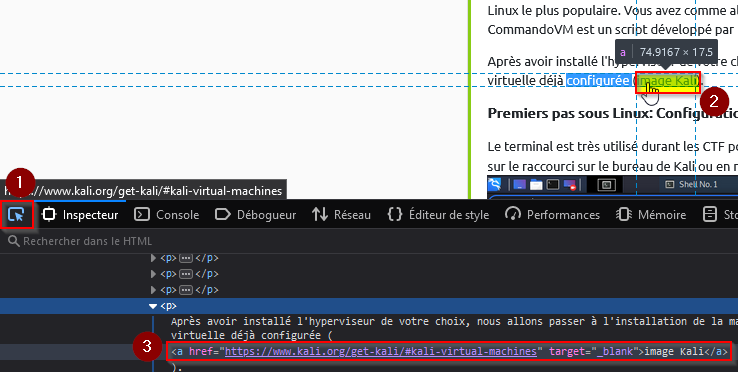
Same, do right click then “inspect” and hover an hyperlink as shown below :
Answer :
1
<a>
Quel est la fonction Javascript utilisé pour écrire un message dans la console (N’oubliez pas les parenthèses -> fonction() )
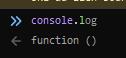
Search in the console or on the web :
Answer : console.log()
Quelle balise HTML indique le début de code Javascript dans le document HTML (Si ça aurait été h1 (celui du titre) vous aurez répondu < h1 >)
View a page source and search for javascript inside :
Answer :
1
<script>
Quel code de statut est retourné par le serveur web pour indiquer que tout c’est bien passé dans la requête HTTP
Press F12 or right click > inspect to have the developper tools, then go to network tab and refresh the page (F5). Keep an eye on the returns status :
Answer : 200
Quelle propriété d’un cookie permet de limiter son utilisation à un site web précis? (Donnez son nom tel qu’il apparait en anglais)
Open the developper tools again and go to storage. Select one of the cookies and look in the attributes :
Answer : domain
BurpSuite
No Answer.
TASK 5 : Web - Fondamentaux
L’URL démystifié
No Answer.
L’HTTP vs. l’HTTPS
No Answer.
C’est quoi un cookie?
Stateless vs statefull + persistence of sessions.
No Answer.
L’utilité du HTML
No Answer.
TASK 6 : Web - OWASP Top 10
OWASP 10
- Injection
- Broken Authentication
- Sensitive Data Exposure
- XML External Entity
- Broken Access Control
- Security Misconfiguration
- Cross-site Scripting
- Insecure Deserialization
- Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- Insufficent Logging & Monitoring
No Answer.
TASK 7 : Web - CTF
Lu
No Answer.
TASK 8 : Forensique
Lu
No Answer.
TASK 9 : Forensique - Outils
lu
No Answer.
TASK 10 : Forensique - Système de fichiers
Lu
No Answer.
TASK 11 : Forensique - Mémoire volatile
Lu
No Answer.
TASK 12 : Forensique - Réseau
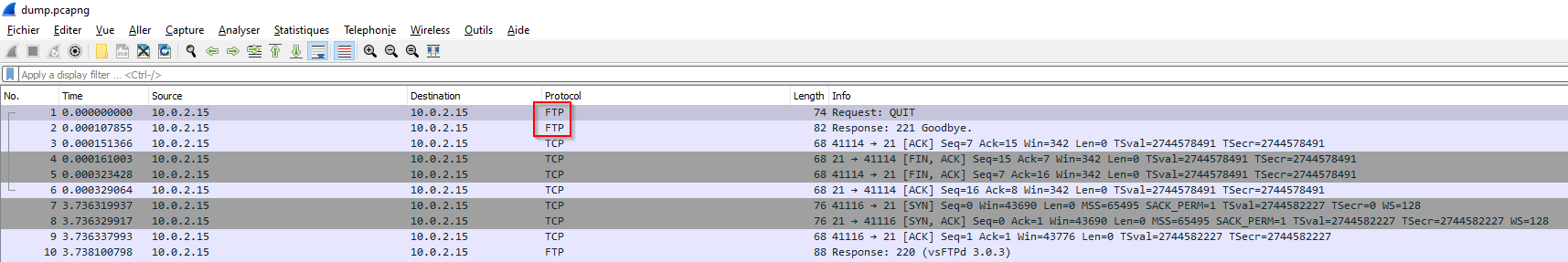
Quel est le protocole de transfer de fichier utilisé ?
Open the dump in wireshark and we got the protocol :
Answer : FTP
Quel est le mot de passe de l’admin ?
FTP is insecure and let us see the password when traffic is sniffed :
Answer : FtP_1S_1NsEcUrE!
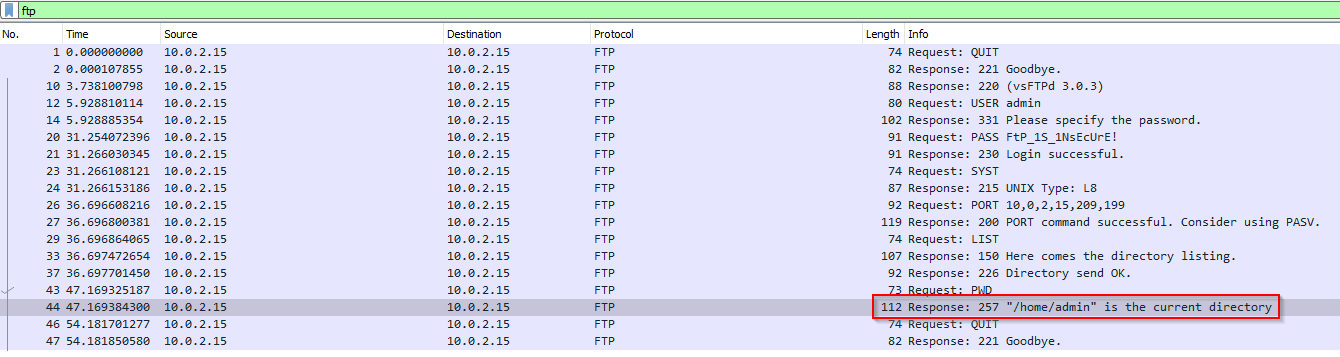
Quelle est le répertoire courant ?
Filtering on ftp to see only traffic which is interesting :
Answer : /home/admin
TASK 13 : Métadonnée
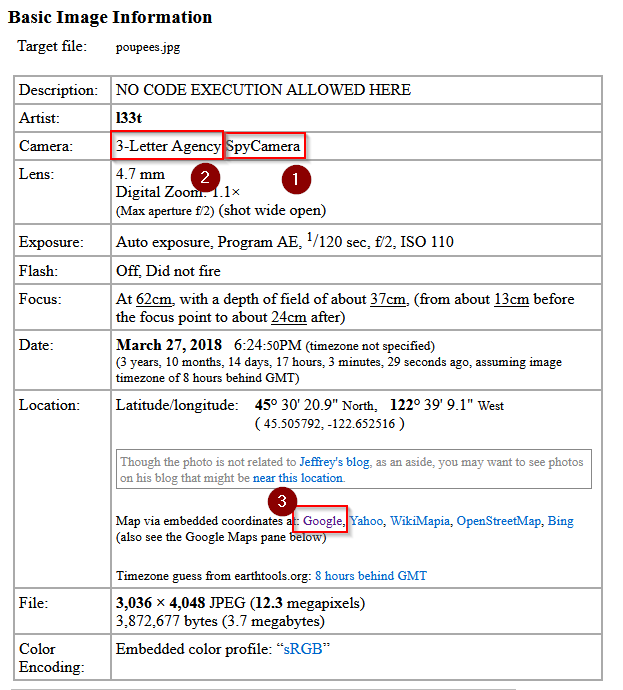
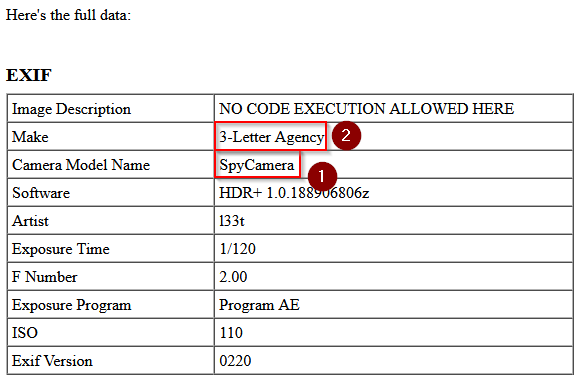
Quel est le modèle de la caméra qui a pris cette photo?
Using Jeffrey’s Image Metadata Viewer http://exif.regex.info/exif.cgi :
or below full data :
Answer : SpyCamera
Quelle est le make de la caméra?
Answer : 3-Letter Agency
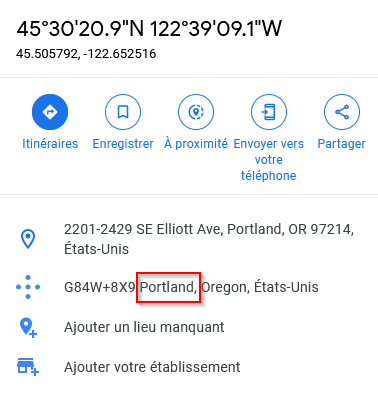
Cette photo a été prise dans quelle ville?
Using the open coordinates with google maps we have :
Answer : Portland
Quel jour la photo a été prise?
Checking back the date in the calendar ;
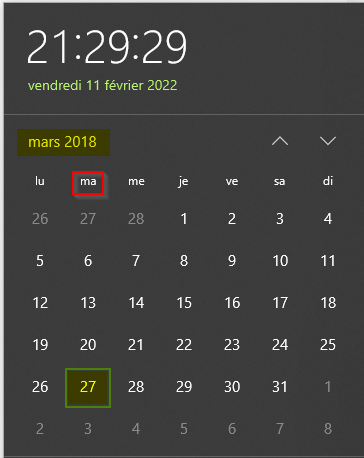 Calendar The answer is in french !!
Calendar The answer is in french !!
Answer : mardi
TASK 14 : Cryptographie
Vous avez probablement remarqué que j’ai utilisé les termes “encodé” et “crypté”. D’après vous, veulent-ils dire la même chose? (répondez par OUI ou NON)
Encoding transforms data into another format using a publicly available scheme so that it can be easily reversed.
Encryption transforms data into another format such that only specific individuals can reverse the transformation.
source ; danielmiessler.com https://danielmiessler.com/study/encoding-encryption-hashing-obfuscation/
Answer : Non
Un exemple de chiffrage que vous utilisez quotidiennement est le HTTPS. En effet, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (https) crypte vos communication en utilisant Transport layer Security (TLS). Ainsi, si un attaquant intercepterait vos communications (attaque “Man in the middle”) avec le site internet, il ne serait pas capable de la déchiffrer et donc n’aura pas accès à l’information envoyée entre ton navigateur et le serveur web.
No Answer.
HTTP chiffre votre communication avec le serveur et garantie l’authenticité du site web contacté. (VRAI ou FAUX)
It’s wrong, HTTPS in the right protocol.
Answer : Faux
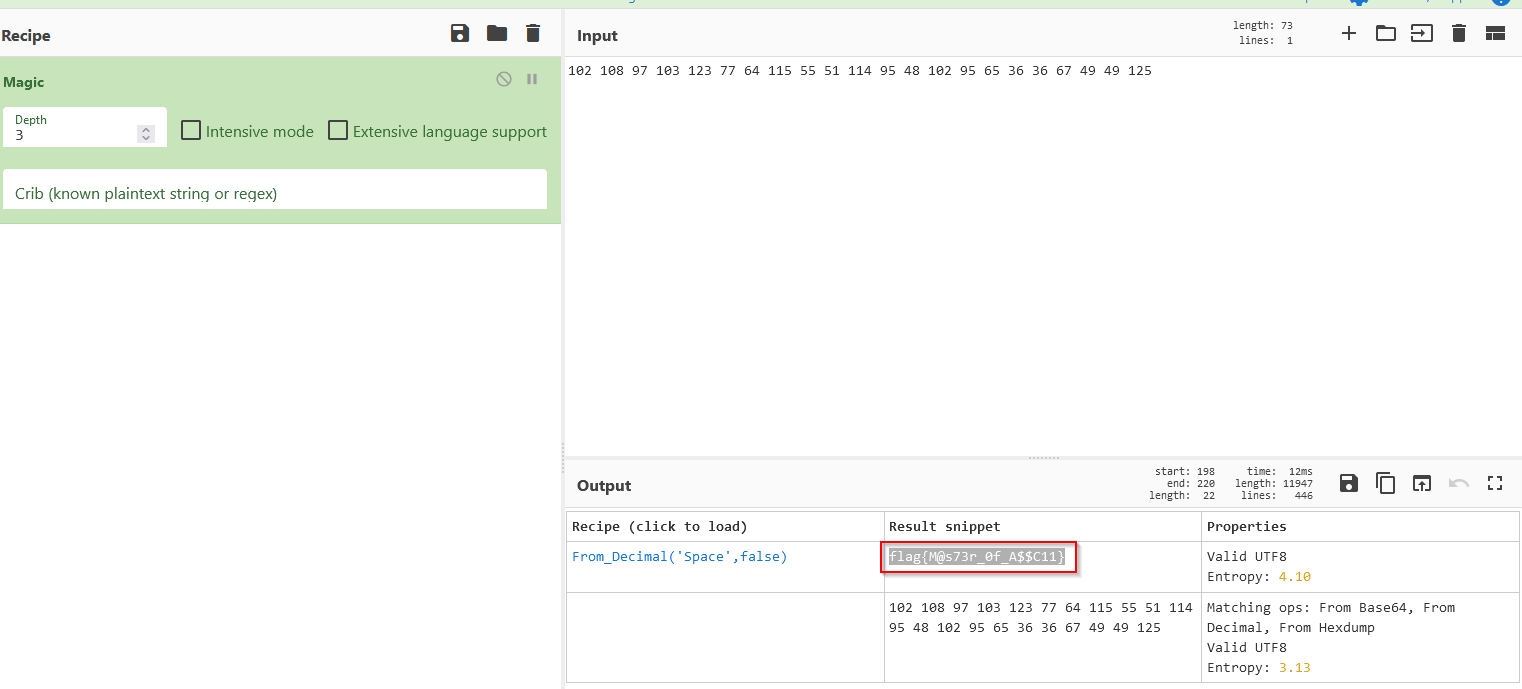
Can you decode this top secret message? 102 108 97 103 123 77 64 115 55 51 114 95 48 102 95 65 36 36 67 49 49 125
Using cyberchef https://gchq.github.io/CyberChef:
Answer : flag{M@s73r_0f_A$$C11}
ENCODAGE URL
No Answer.
UNICODE
No Answer.
Le XOR peut alors être utilisé pour chiffrer un message. Il suffit de XOR le message avec une clé de même taille comme vu dans l’image.Il est important par contre de respecter quelques critères pour assurer la robustesse de ce chiffrement.
- avoir une longue clé secrète qui est non-répétitive
- avoir une clé généré aléatoirement pour chaque nouvelle communication
- la clé doit être maintenu
No Answer.
CHIFFRAGE ASYMÉTRIQUE
No Answer.
CHIFFRAGE SYMÉTRIQUE
No Answer.
Télécharger le fichier pdfencryption.pdf. Quel est le contenu de ce fichier ?
I used john the ripper to brute force the password :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[/opt/JohnTheRipper/run]
└─$ ./pdf2john.pl /home/kali/Documents/THM/ecoleCTF/encryption.pdf > /home/kali/Documents/THM/ecoleCTF/encrypt.hash
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/THM/ecoleCTF]
└─$ cat encrypt.hash
/home/kali/Documents/THM/ecoleCTF/encryption.pdf:$pdf$2*3*128*-4*1*16*733fb6d05e1aa24fb646300e91994d30*32*a709e10baf63f670f2b1694f2d1fb4380122456a91bae5134273a6db134c87c4*32*475fa4a10e5308c40de79c8b35f7406ccf53009f5d15ae3d70e0c1491ceef762
──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/THM/ecoleCTF]
└─$ john encrypt.hash
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (PDF [MD5 SHA2 RC4/AES 32/64])
Cost 1 (revision) is 3 for all loaded hashes
Will run 4 OpenMP threads
Proceeding with single, rules:Single
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
Almost done: Processing the remaining buffered candidate passwords, if any.
Proceeding with wordlist:/usr/share/john/password.lst
thunderbird (/home/kali/Documents/THM/ecoleCTF/encryption.pdf)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE 2/3 (2022-02-11 18:34) 1.960g/s 104047p/s 104047c/s 104047C/s leslie..crawford
Use the "--show --format=PDF" options to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
I use this password to open the pdf file and found the flag :
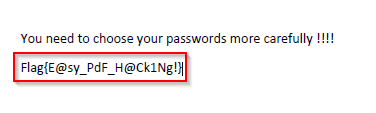
Answer : Flag{E@sy_PdF_H@Ck1Ng!}
TASK 15 : Stéganographie
Maintenant que vous comprenez le concept de LSB, pouvez-vous dire quel byte est plus grand ? 100000 ou 11111
Answer : 100000
Maintenant que vous savez comment cacher des messages, pouvez-vous décoder la lettre et le chiffre correspondant en hexadécimale qui est caché dans cette suite binaire: (P.S. Le processus de décodage est le même que celui d’encodage mais à l’inverse)
- 1001010010101011001001111001100000010001001100100100010110110111
- répondre avec ce format: lettre=chiffre=binaire
- (chiffre en hexadecimal)
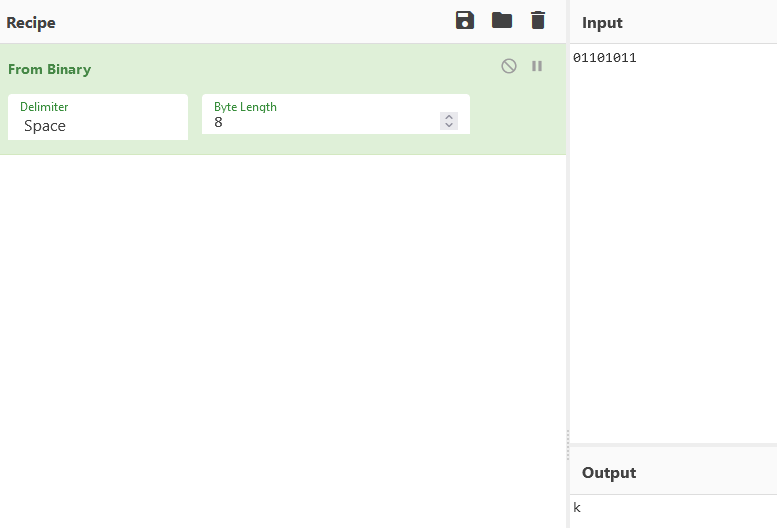
Rearrange the 0 and 1 by octet :
1
10010100 10101011 00100111 10011000 00010001 00110010 01000101 10110111
then all least significant bit are :
1
01101011
Which convert with cyberchef from binary correspond to the letter k :
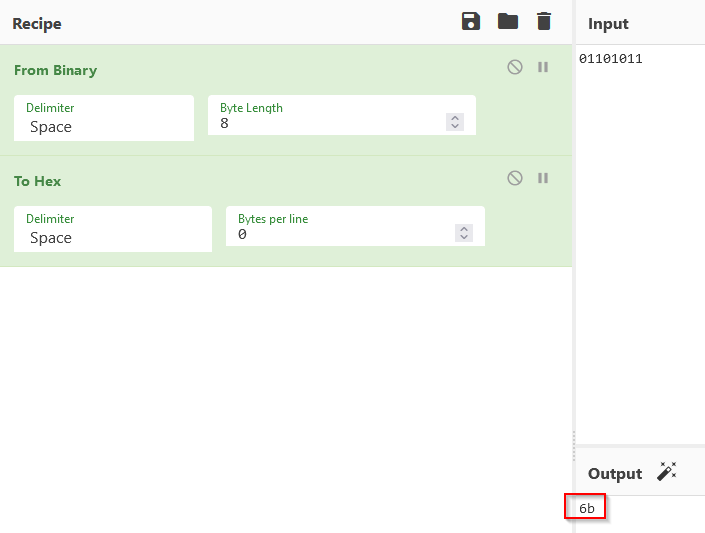
Then converting this to hex :
giving the answer in the format letter=hex=binary
Answer : k=6b=01101011
TASK 16 : Pour aller plus loin
lu
No Answer